“In the future I am going to do something that scares me more often.”
Big Ideas Fest 2014 Participant
Reflections like the one above are what keep me coming back every year as a designer and facilitator of ISKME’s Big Ideas Fest — an annual immersion in collaboration and design for educators around the world looking to make meaningful change in teaching and learning.
As someone who works behind the scenes, as well as in the midst of the action, I am always thrilled to see the diverse collection of educators arrive with enthusiasm, some with a degree of healthy skepticism, and leave Big Ideas Fest as experienced BIFniks— open, collaborative, and hopeful education change makers, equipped with new tools and concepts, and inspired to put them into practice in their own learning environments.
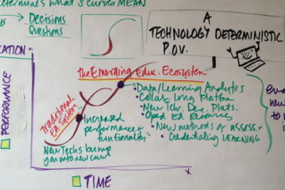
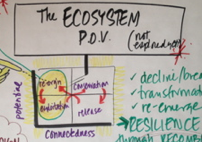
The Action Collab—ISKME’s design thinking process— frames the Big Ideas Fest experience as it gives BIFniks a chance to immerse themselves in an innovation and collaboration experience in order to learn it and apply it to real world education challenges. It provides a common language for the way we interact, pose questions, and look ahead to post BIF engagements.
We asked BIFiks to reflect on their Big Ideas Fest experience at its conclusion to learn about the impact of the BIF and Action Collabs on their work. Three important outcomes, listed below, emerged from their comments about their Action Collab experience.
It demystifies and democratizes innovation by breaking it down into practical activities
BIFniks leave with a grounded experience in creative problem-solving and with an understanding of how to set themselves up for innovating at home. They learn to become open collaborators less concerned about perfection and more focused on generating possibilities to explore.
Today I learned:
“How to move forward from a juicy question to a specific innovative solution.”
“Letting go of my own outcome leads to new discoveries.”
“The design process is messy but generative.”
It instills fearlessness and confidence in their own abilities as creative problem-solvers
They learn how to trust their own creative instinct and gain an appreciation for the uncertainty and surprise factor that accompanies true innovation.
My biggest take-away is:
“There’s something productive behind frustration!”
“You can’t predict where an idea will go.”
“I can’t be wrong, my ideas matter.”
It gives them skills and practices to act on right away
BIFniks walk away with clear, practical tools for collaborating and unlocking creativity in themselves and their colleagues.
In the future I’m going to:
“Live ‘Yes, And’ more often.”
“Resist suppressing my creativity.”
“Listen in order to receive”
“Use student collaboration right away in my own work.”
I’m looking forward to our upcoming Facilitator Training for Action Collabs on April 27-28, 2015 in San Francisco. If you want to learn how to facilitate an Action Collab process in your own organization, ISKME is offering a 2-day immersive training where you will learn the Action Collab process and its rationale, by participating in an Action Collab, and learning how to set up Action Collab modules for your own groups. Check out the following announcement for more details, and email andrea@iskme.org if you have additional questions.